What Is Injection Molding, Extrusion Molding & Blow Molding, What Are Differences?
Injection molding, extrusion molding, and blow molding are the three main plastic processing techniques. The choice of manufacturing method depends on the material properties and product structure. Let’s take a closer look at these three commonly used plastic forming processes.
First of all, the raw materials used in these three molding methods all belong to thermoplastic materials. The characteristics of this type of material is that they are moldable at a certain temperature. After cooling, they can quickly solidify and can be reprocessed into new products after recycling.
What Are Thermoplastics?
Thermoplastic is a type of plastic that can be softened by heating and solidified by cooling. Thermoplastics have several distinct characteristics and advantages.
One of the main features of thermoplastics is their thermoplasticity – the ability to soften when heated and reharden when cooled. This allows thermoplastics to be easily reshaped and reprocessed multiple times simply by heating and cooling. When heated, thermoplastics return to a fluid or pliable state that allows them to be molded or reshaped. Upon cooling back down, they solidify and maintain their newly formed shape.
Another advantage is that thermoplastics are recyclable. Waste plastic material from thermoplastic products can be regrround and reheated then remolded, since heating returns the plastic to its fluid state. This makes thermoplastics highly sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Thermoplastics also have lower processing costs compared to other plastics, as they do not require chemical hardeners to solidify permanently into the final shape. Simple heating and cooling is enough to achieve shape transformations in thermoplastic materials.
What Is Injection Molding?
From its name, injection molding injects plastic into a mold. A mold that matches the product design can be used to manufacture plastic products as needed. Injection molded products are widely used in our daily lives and work. It can be said that we use various injection molded products every day. The injection molding process involves heating and softening the raw material and then using a screw to rotate and pressurize it, injecting it into the mold cavities. Once the plastic is fully filled, it cools and sets in shape. The core pin then ejects the product from the mold, and manufacturing is complete.
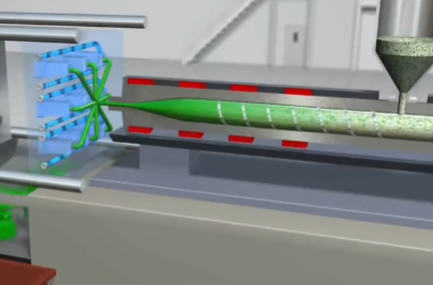
What Is Extrusion Molding?
As the name suggests, extrusion molding applies a certain force to extrude the raw material. It can be seen that the fluidity of the material is not very good, which can realize continuous production. Production efficiency is very high. Pipes, plastic boards, profiles and other shapes can be produced by extrusion molding. Like injection molding, the raw material is first heated and softened and then extruded through a screw or piston to shape through the tool head mold. The product extruded from the mold will continuously lengthen. After cooling, it will be fixed in shape. It can then be cut to the required length to obtain the finished product.
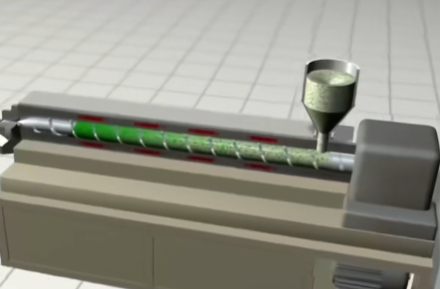
What Is Blow Molding?
Blow molding is also known as hollow molding. In blow molding, compressed air is blown into a closed mold to make the material diffuse outwards and tightly attach to the inner walls of the mold cavity to form a hollow shape. Containers such as beverage bottles, milk bottles and oil drums are manufactured using blow molding techniques. Like the first two processes, the raw material also needs to be heated and softened first, and then pressed into the mold cavity. Then air is blown into the mold to shape it. After cooling, a hollow plastic product can be obtained.
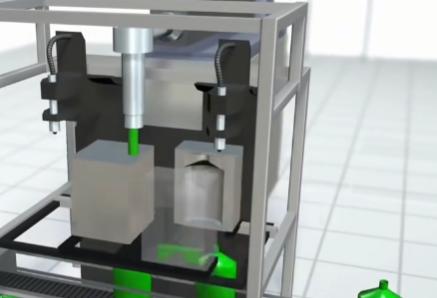
Differences Between 3 Plastic Forming Processes
| Process | Injection Molding | Extrusion Molding | Blow Molding |
| Raw material fluidity | Raw material needs to be melted and highly fluid | Raw material needs to be softened and moderately fluid | Raw material needs to be softened and moderately fluid |
| Forming mechanism | Injecting fluid plastic into a closed mold | Squeezing softened plastic through a mold | Blowing air into a closed mold to shape the plastic |
| Applicable products | Components, daily-use products | Boards, pipes, thin-walled profiles | Containers, bottles |
| Production efficiency | High but mold cost is high | Very high and continuous production | General but product structure is complex |
| Cost | High mold cost but low per-unit cost | Low mold cost and high production efficiency | Low mold cost but air pressure adds cost |
| Product structure | Complex shapes are difficult | Limited to elongate profiles | Can form complex hollow shapes |